Your Cart is Empty

December 08, 2020 5 min read
Geographically, the gut and the brain are pretty far apart but biochemically, they are closer than you'd think. The gastrointestinal tract, or GI tract, is what carries your food all along the digestive journey, starting with the mouth. This includes everything from your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus, and literally everything in between. The gut is a part of this system; usually when someone refers to the gut, what they really mean is the intestine or digestive system where food is broken down and absorbed by the body - this is where all the gut-brain talking starts.
The gut, or gut microbiome, is responsible for digestion. It's trillions of gut microbiota act as the gatekeepers as to what can pass through the intestinal walls to be absorbed by the body. Trillions of gut bacteria, viruses, and even fungi fill your digestive tract. In fact, there are more bacterial cells in your body than there are human cells! Bacteria often seems like a bad word, but it's these good bacteria and gut microbes that help to communicate with your brain, protect your immune system, and of course, digest your food.
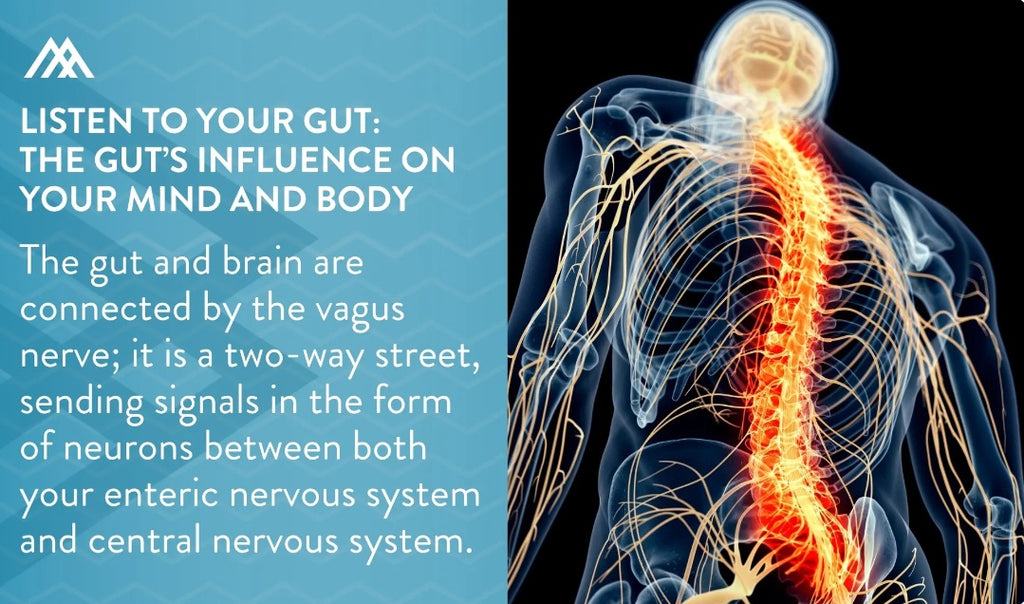
The gut and brain are connected by the vagus nerve; it is a two-way street, sending signals in the form of neurons (nerve cells) between both your enteric nervous system and central nervous system. Here's a mind-blowing (or rather gut-blowing) fact for you: the gut contains 500 million neurons, hence why it's often called the second brand. Of course, the brain does most of the heavy lifting of passing along information with its 100 billion neurons, but the signals sent from the gut are nothing to turn your nose up at!
The gut-brain axis also communicates by way of neurotransmitters. There are four main neurotransmitters in the brain:

Normally when we think neurotransmitters and mood management, we don't reflexively think "gut" but surprisingly, a large proportion of our body's neurotransmitters, and especially serotonin, are produced in the gut. The third way your brain and gut are connected is via the immune system. Microorganisms in the gut help regulate the body’s immune response and reduce inflammation.
Have you ever noticed how the gut reacts to stress? Oftentimes, whenever we feel nervous or anxious, our brain's stress response triggers a reaction in our gut. Nausea, heartburn, constipation, or even that "butterflies in your stomach" gut feeling often accompanies public speeches and first dates. This reaction is more instantaneous, but your gut can have long-term effects on your brain as well.

Individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease are hit the hardest by the effects of stress. Inversely, flare-ups of IBS can also be triggered by stress, showing the two-way communication between the enteric and central nervous systems. Your gut helps to stave off inflammation that can negatively affect your brain health and cause conditions such as Alzheimer’s, depression, autism, and dementia. Gut dysbiosis, or too many unhealthy gut bacteria, can cause weight gain and inflammation as well.

In order to support your brain and gut's well-being so it can keep pumping out neurotransmitters and keep your gut microbiome at peace, you need to feed your gut the right things. Probiotics, prebiotics, and psychobiotics can all be consumed or supplemented to support the health of the bacteria already in your gut, as well as to produce new healthy bacteria. Prebiotics are fibers that ferment and stimulate the production of probiotics in the gut. Probiotics are live microorganisms that when consumed help your gut microbiome to flourish. When they affect your brain, they are called psychobiotics.
Some probiotics (or psychobiotics) have been proven to help reduce the symptoms of depression and anxiety. Others can help to manage IBS, which has a ripple effect on your brain health. Probiotics can be taken in supplemental form or through your diet. When shopping for a probiotic, be wary as not all products are created equally; look for the good bacteria "bifidobacterium" and/or "lactobacillus" in the ingredients list. These two probiotics are used to help manage irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, and ileal pouches and are needed in every gut to help support digestion.

If you choose to go the diet route, make sure to eat whole grains, nuts, vegetables, and fruits that are high in fiber. Fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, and kombucha, have been shown to alter brain activity. Omega-3s and foods high in fatty acids have also been shownto help the gut microbiota flourish while helping to manage brain disorders.
Lastly, you can strengthen the intestinal walls and help manage leaky gut syndrome by increasing your intake of collagen. Type III collagen is concentrated primarily in the intestines and puts its amino acid glutamine to work to strengthen the walls of the intestines and reduce inflammation. You can mix collagen protein powder in with polyphenol-rich foods such as green tea and coffeeto support cognition and encourage more healthy gut bacteria to grow.
Protecting your gut also means looking out for your mental health. Listening to your gut isn't just a hunch or superstition - it's science!
The gut and brain are connected by the vagus nerve; a two-way street, sending signals in the form of neurons (nerve cells) between both your enteric nervous system and central nervous system.
A large proportion of our body's neurotransmitters, and especially serotonin, are produced in the gut.
The brain and gut are connected via the immune system.
Microorganisms in the gut help regulate the body’s immune response and reduce inflammation.
Flare-ups of IBS can also be triggered by stress, showing the two-way communication between the enteric and central nervous systems.
Probiotics, prebiotics, and psychobiotics can all be consumed or supplemented to support the health of the bacteria already in your gut, as well as to produce new healthy bacteria.
Omega-3s and foods high in fatty acids have also been shown to help the gut microbiota flourish while helping to manage brain disorders.
Take our quiz and find which supplements your body is craving.
